Configuring GrowthBook to work with BigQuery
This document outlines the steps needed to add your BigQuery database to GrowthBook.
1. Create a service account for GrowthBook
Within your Google Cloud console account, create a service account for GrowthBook to use
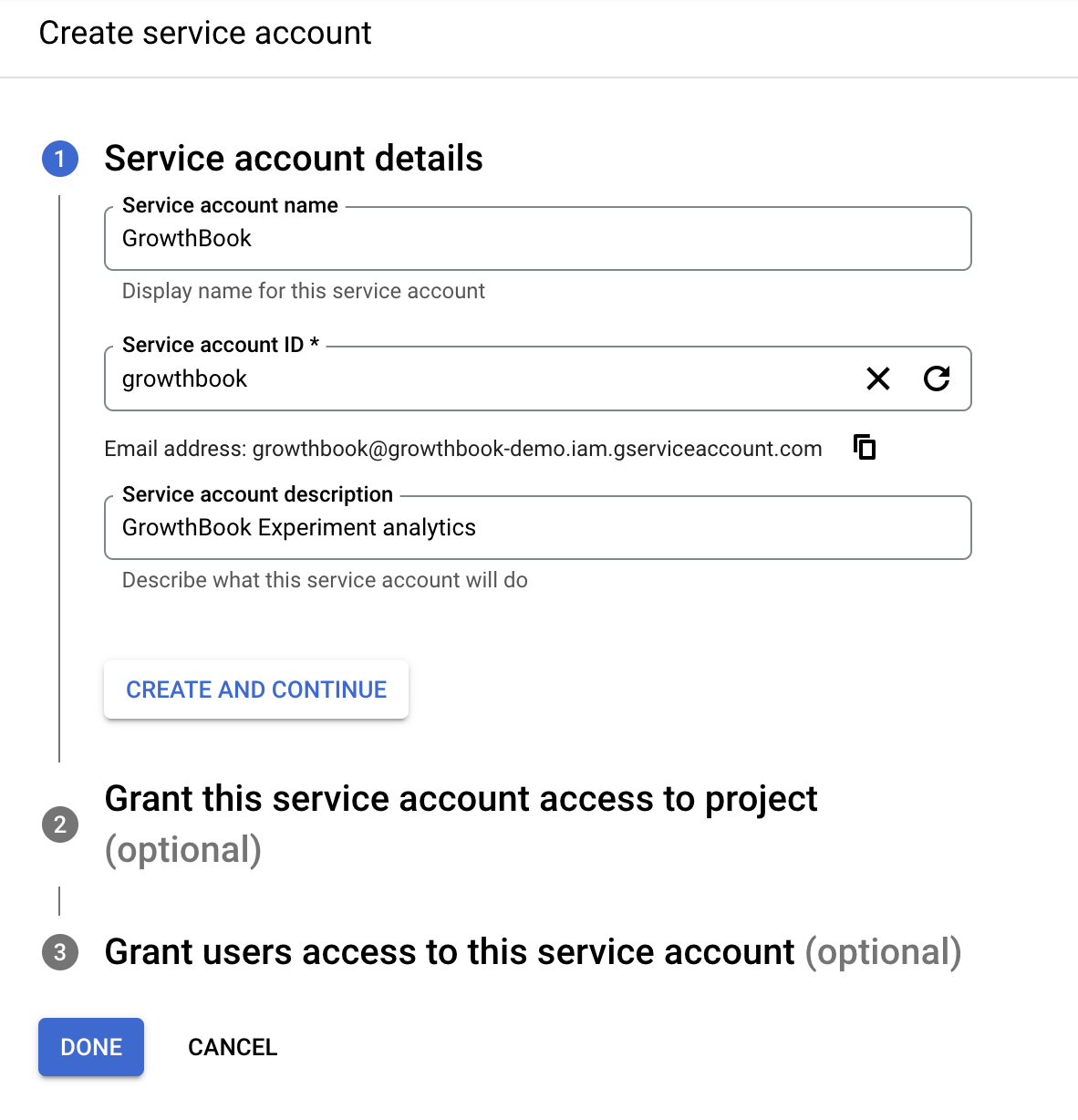
Create a service account name and account ID. On the next page you need to add 3 specific roles:
On the Grant page, add the following three permissions roles for read-only access:
- BigQuery Data Viewer
- BigQuery Metadata Viewer
- BigQuery Job User
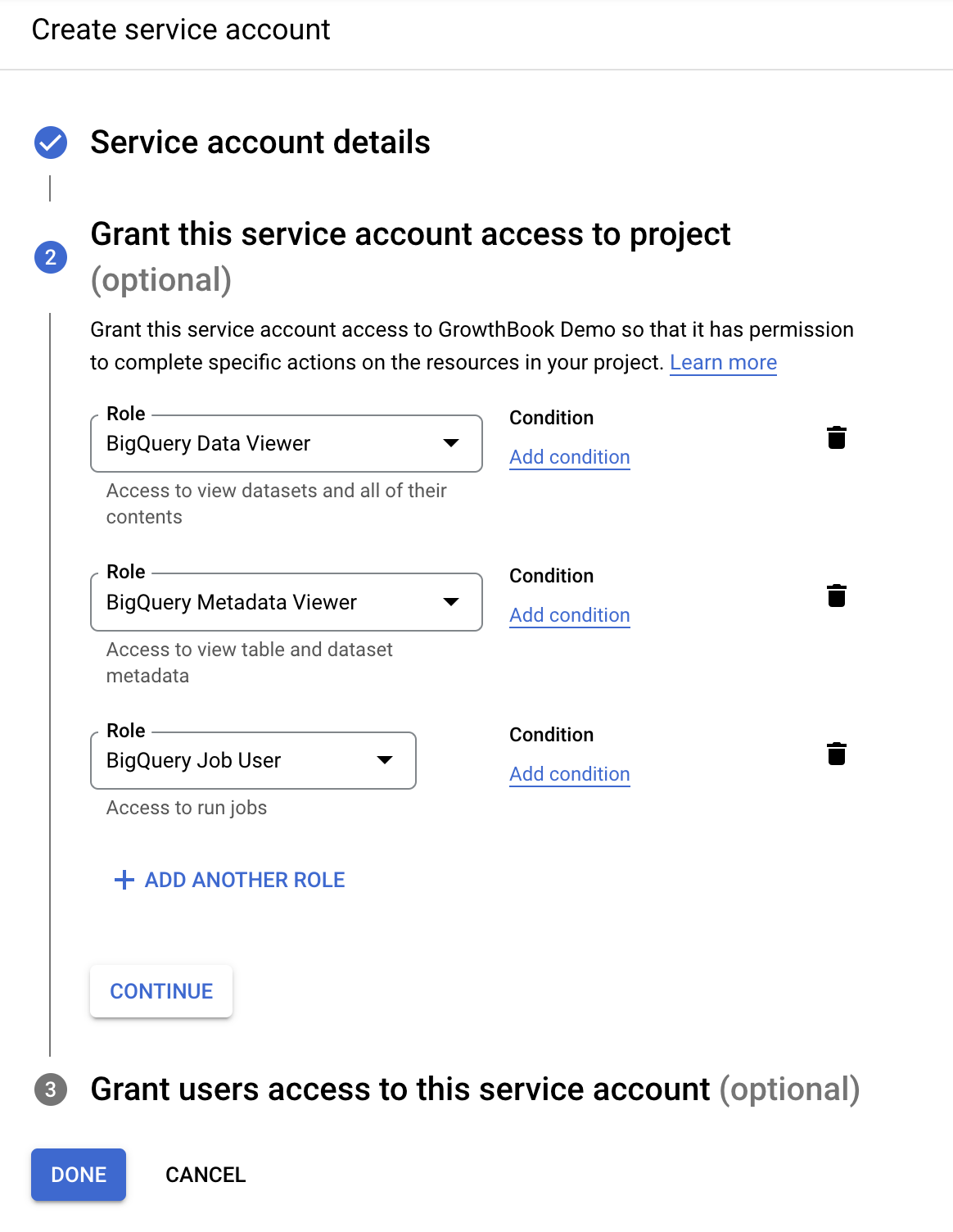
On the final page when creating a service account, you can skip the optional fields.
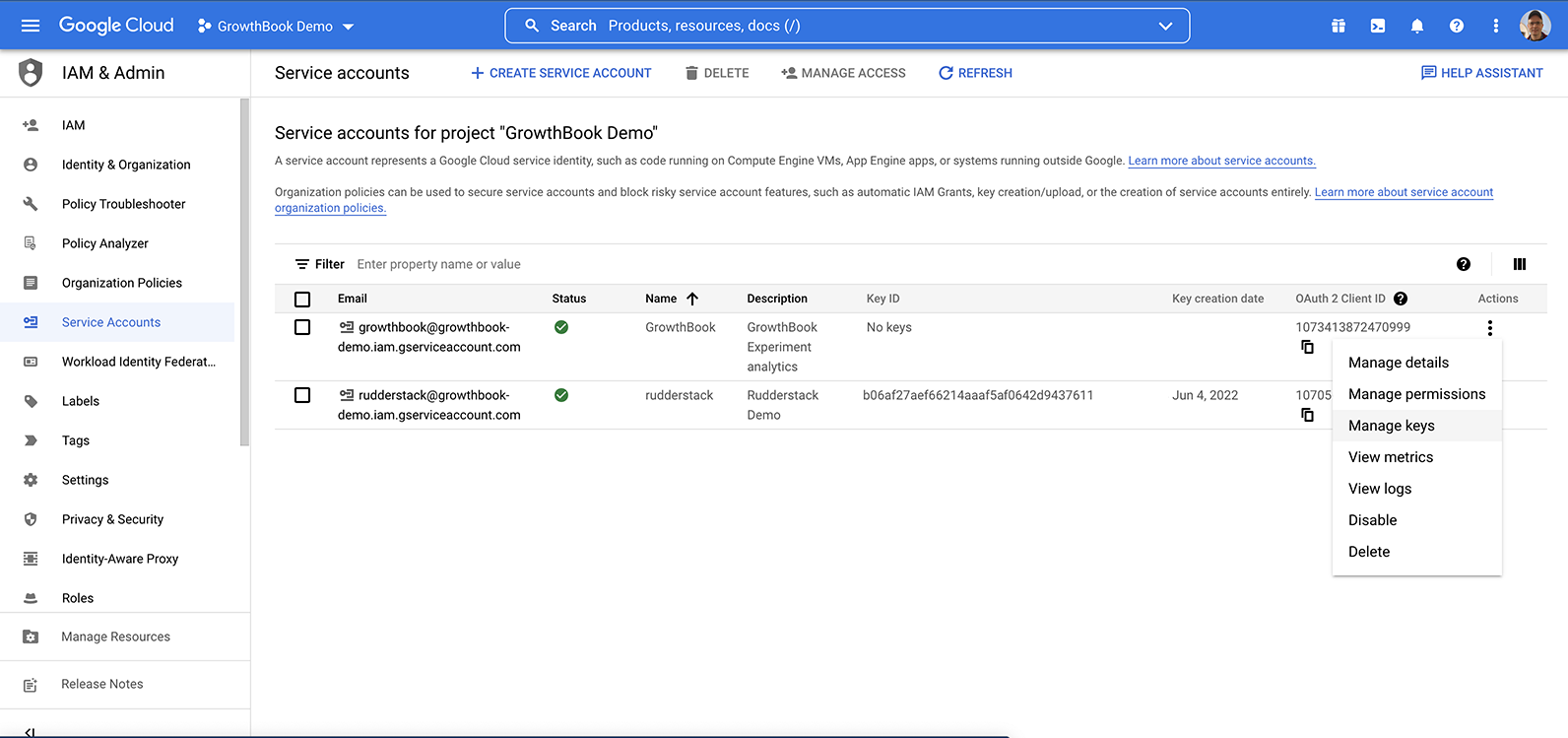
You should see the new service account listed, without a Key ID. We need to add an access key to this account so the
credentials can be added to GrowthBook. Click on actions, and select Manage Keys.
There are two ways to provide credentials to GrowthBook:
- Auto-discovery from environment variables or GCP metadata (only available when self-hosting)
- Upload a JSON key file for the service account
We're going to show how to do the JSON key file method. On the keys page, add a new key, and select JSON.
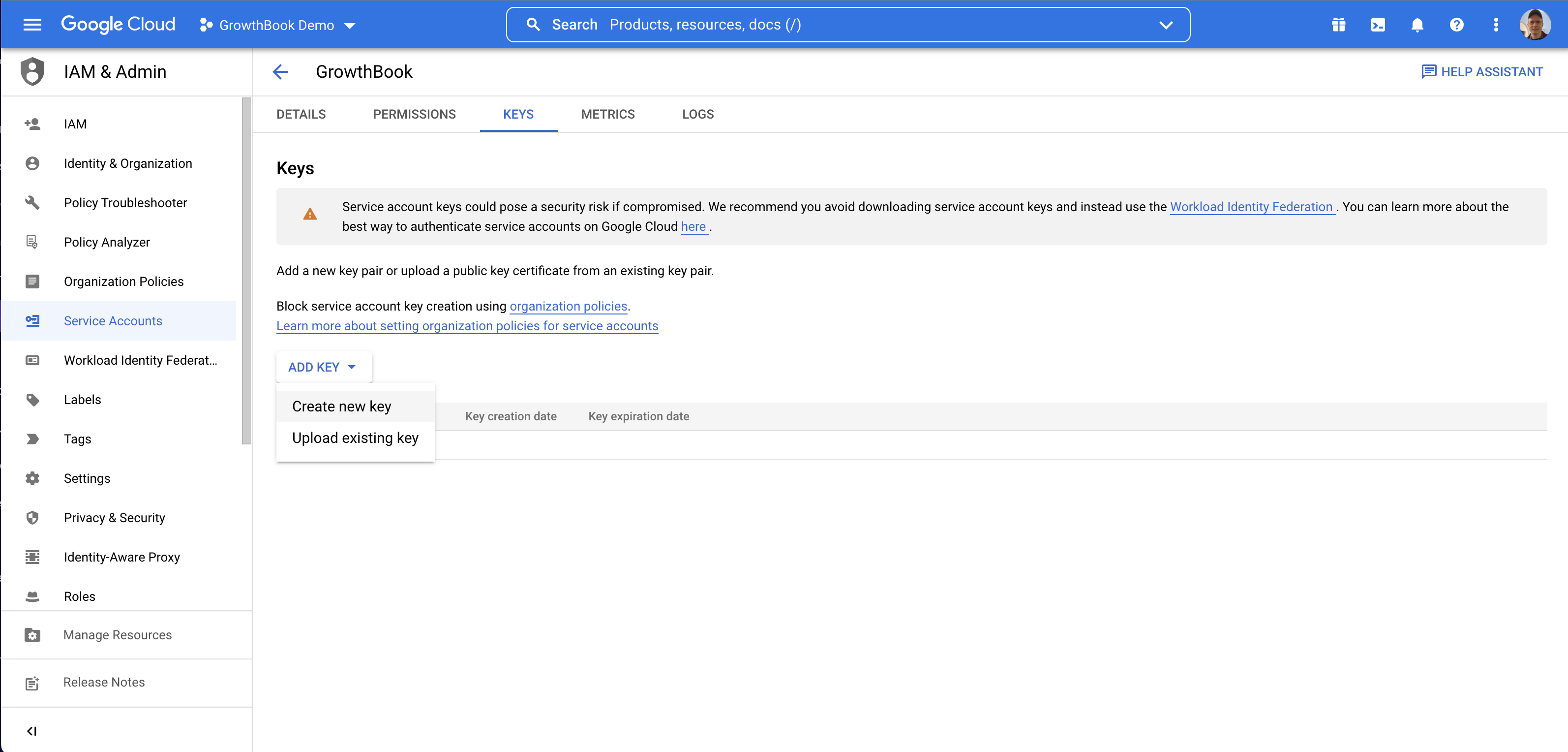

This will cause the JSON key to be downloaded to your computer.
2. Connect GrowthBook to BigQuery
From the Analysis -> Data Source page, click on add new data source and select the event tracker you're using. If your event tracker is not listed, or you're using something custom, click on the "Custom" button at the bottom.
Selecting an event tracker here will pre-populate the experiment exposure query which is need to determine which user saw which experiment variation. Depending on your needs, you may still need to adjust these queries to match your specific schema.

Select BigQuery as the data source type.
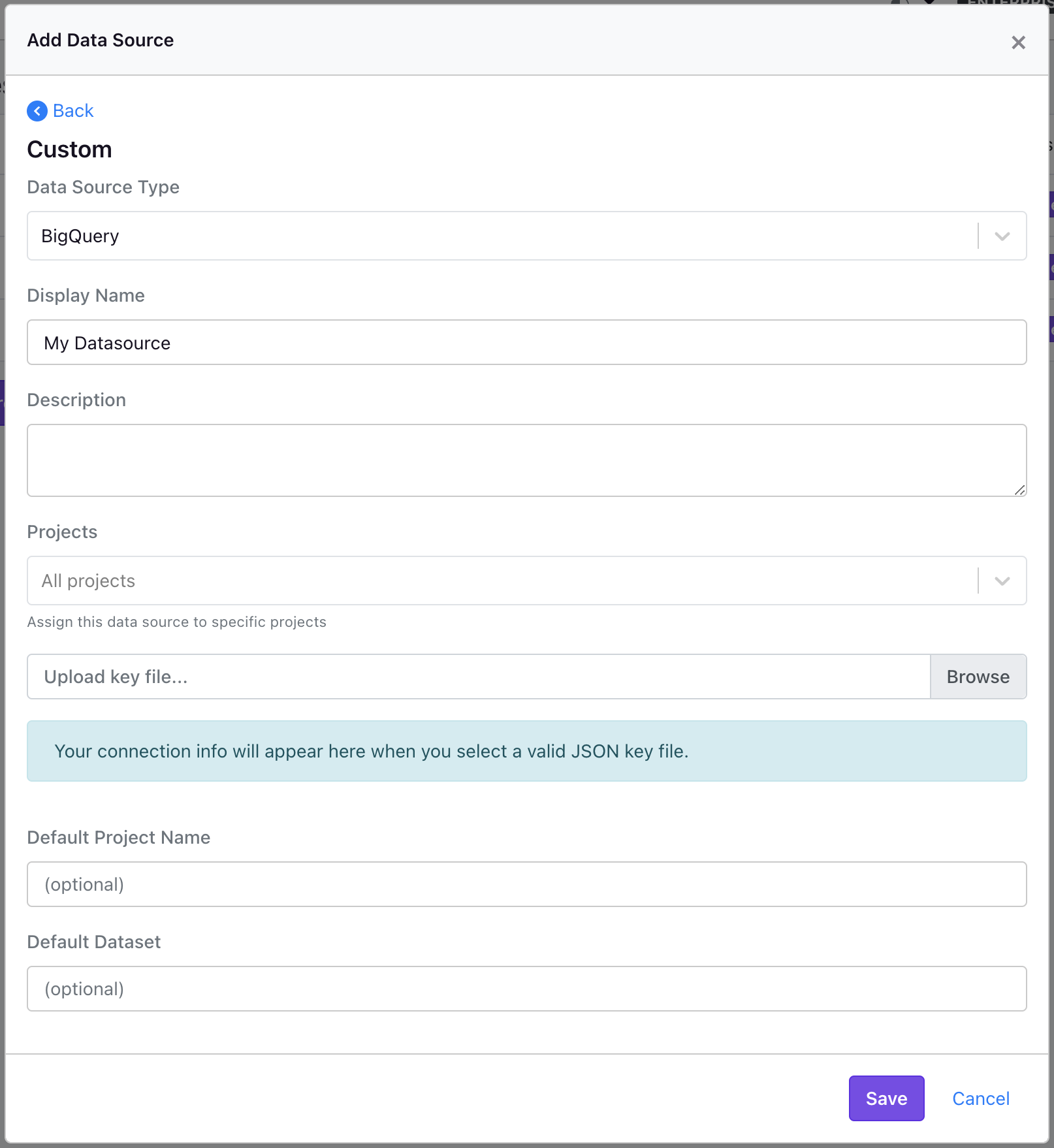
Add the names you'd like to use, and select the JSON key file that was downloaded earlier.
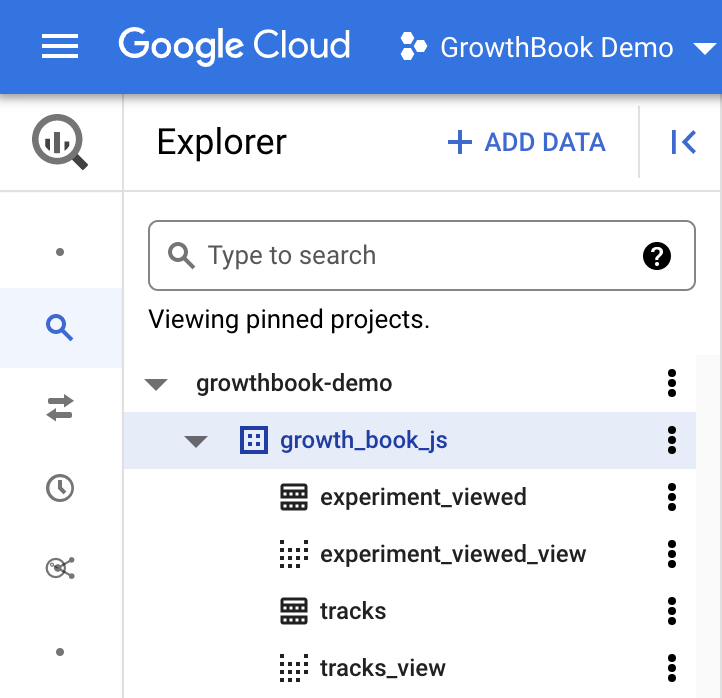
Although the Default Project Name and Default Dataset is not required, it is helpful to set this to the correct
values for your database. You can get the name of these fields from the Google Cloud explorer. You will see the top level
project name, and when expanded, find the dataset which has your experiment exposure table (which will be experiment_viewed if you use Segment or Rudderstack).
When you click save, GrowthBook will test the connection to make sure the credentials are correct. If the connection is successful, you should see a success message on the next page.
Monitoring GrowthBook query cost
Whenever we query your BigQuery database we add { integration: "growthbook" } as a label to the query job to make it easy for you to monitor cost or filter GrowthBook query jobs by label for other use cases.
Read more about how to group by label value for a specific key here.